In this problem, you are given a process that runs indefinitely and blocks the program. The only way to stop the program is to send a SIGINT. But you should stop the process gracefully first. If you receive SIGINT again, then kill the process immediately.
Solution
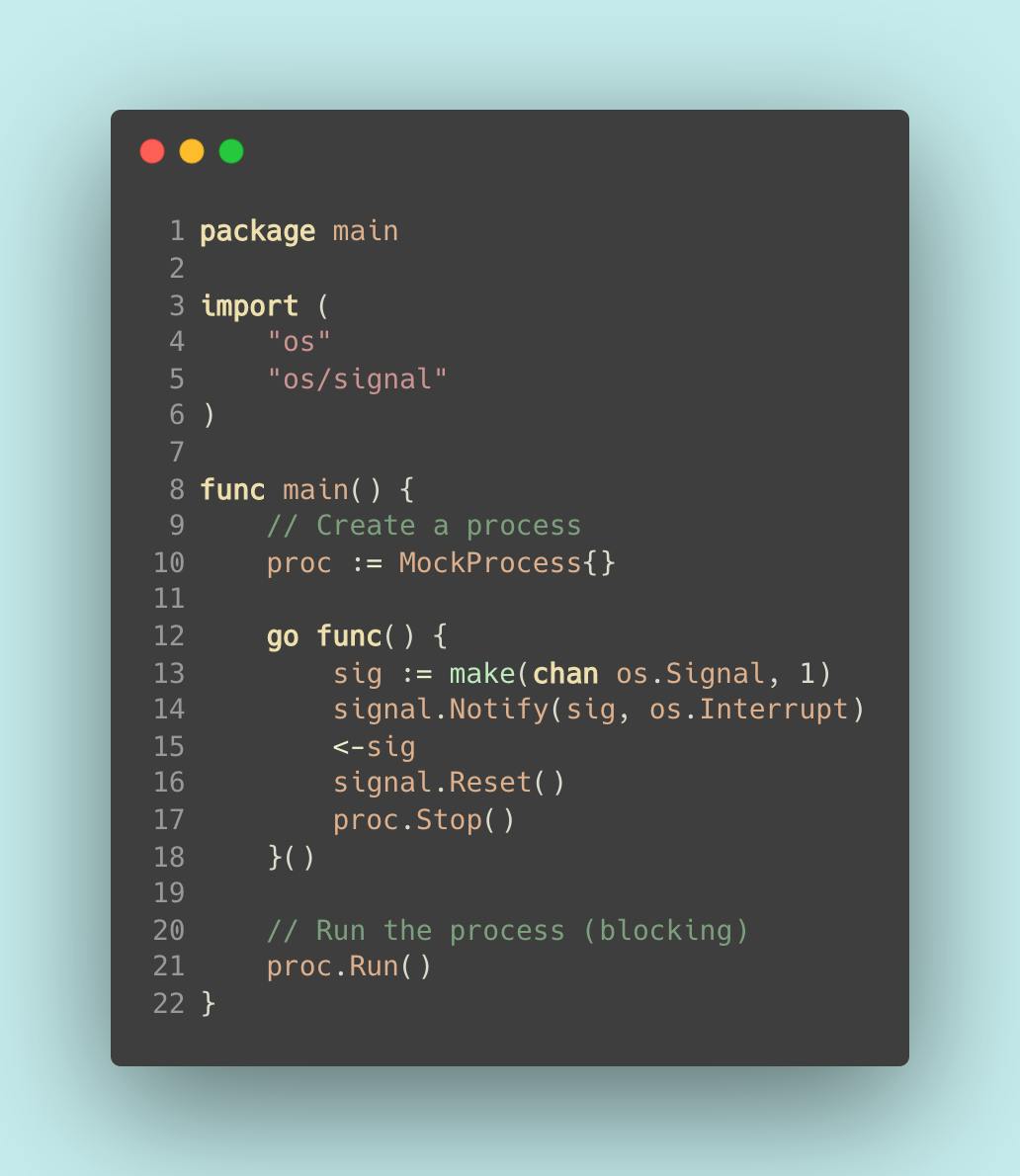
Line:
- This goroutine executes a blocking receive for the operating system signal.
- Create a channel to receive
os.Signalvalue. This channel should be buffered. - Register the channel to receive a notification. We use
os.Interruptinstead ofsyscall.SIGINThere so Go can handle the correct interrupt on the platform it is running on (operating system Agnostic). - Block until we receive a signal.
- Remove all signal handlers. The
sigchannel will no longer receive any signal. So the next time the user press Ctrl-C, it will follow the default behavior of signals in a Go program. In this case, the SIGINT signal causes the program to exit. - Gracefully ask
procto kill itself.
Key takeaways
A little background
In a Unix-based operating system, processes can receive a variety of signals. Signals are the method of communication between processes. There are a lot of signals. For example we have SIGTERM, SIGQUIT, SIGKILL, etc.
When a process receives a signal, it interrupts its execution, and a signal handler is invoked. Every signal has a default action: ignore, kill the process, kill the process and make a core dump file, stop the process, and resume operation.
- SIGINT is the signal sent when you press Ctrl+C. The default action for the signal is to kill the process.
- SIGTERM and SIGQUIT are used to terminate a process. SIGTERM is the default signal when we use the
killcommand. Sometimes, when we send SIGTERM, the process does a clean-up routine before exiting. - SIGKILL is also used to terminate a process. SIGKILL can't be ignored and can not be changed by a program. So your Go application will not handle this signal. The process that receives SIGKILL might not execute any clean-up routine.
Go os and os/signal packages
You can use the os package to work with the operating system. This package provides a platform-independent interface.
You can use the os/signal package to handle the operating system signal. This package implements access to incoming signals. Signals are primarly used on Unix-like systems. But you can still use this on Windows. According to the documentation:
If Notify is called for os.Interrupt, ^C or ^BREAK will cause os.Interrupt to be sent on the channel, and the program will not exit.
How to capture signal pattern in Go
Create a goroutine that runs a blocking for os.Signal, where you:
- Create a buffered channel.
- Use
signal.Notifyto register what signal you want to capture and specify the channel that receive the signal from step 1. - Block for the signal to be received.
- Do what you need to do with the signal.


